What is BioChemical Pregnancy? How is it Confirmed?
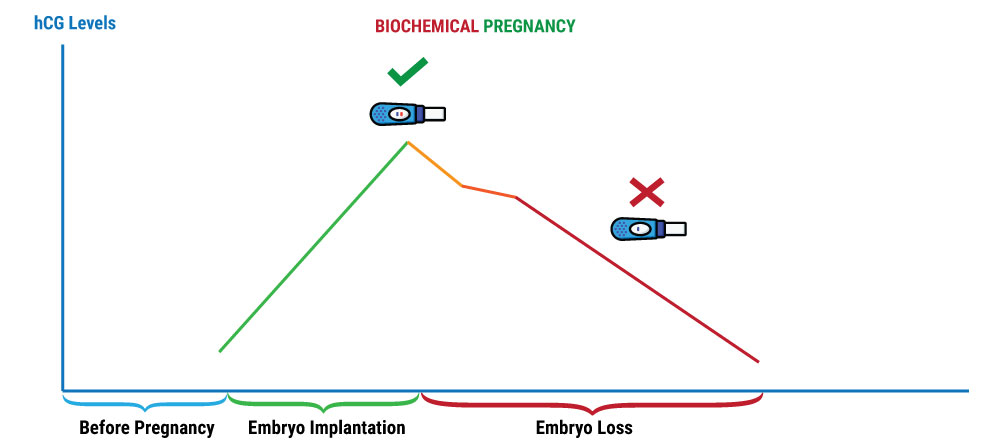
A biochemical pregnancy is a pregnancy which has detectable hCG (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin Hormone) tested through Blood or when Urine Pregnancy Test is Positive for pregnancy but the pregnancy does not develop enough to be seen on ultrasound by the IVF specialist.
Biochemical pregnancy is therefore diagnosed on the basis of a Blood Test and Ultrasound by an IVF specialist.
Biochemical pregnancy is also known as – Pre Clinical Embryo loss or Chemical Pregnancy.
All chemical pregnancies are, by definition, unsuccessful and the only evidence of the early pregnancy is the measurement of hCG in a woman’s blood or urine. Ultrasound done by an Infertility specialist at any point of time will not reveal any evidence of such pregnancy.
Is Bio chemical pregnancy and miscarriage same?
No, they are different. A biochemical pregnancy is confirmed by an IVF specialist before clinical stage of pregnancy and therefore called Pre-Clinical Pregnancy or Chemical Pregnancy. A chemical pregnancy is a term used to describe a very early miscarriage which occurs before the fifth week of gestation and well before the fetus can be visibly detected on an ultrasound. A chemical pregnancy is believed to affect as many as 75 percent of pregnancies that end in miscarriage.
Is it a True or a False pregnancy?
It is a true pregnancy in the sense that it results after fertilization of an egg and sperm, but it fails to progress very early on, and hence even before it can be seen on an ultrasonogram it gets miscarried.
What is Biochemical miscarriage?
Technically all biochemical pregnancies are very early miscarriages, occurring mostly before 5th week of pregnancy. They tend to miscarry spontaneously even before they are being detected on a sonography.
What are the reasons for Biochemical pregnancy?
In most cases, IVF specialists are unable to identify the exact cause of biochemical pregnancy. In some cases, the causes are as follows: Genetic abnormality in embryo, Abnormality in thickness or pattern of endometrium, Immunological or hormonal imbalance.
How common are biochemical pregnancies?
- Biochemical Pregnancies occur in between 8% and 33% of all pregnancies and 18%–22% of IVF pregnancies.
- Since biochemical pregnancy rate falls somewhere between 13-22% in healthy fertile women, it means at least 1 in 5 women may experience a biochemical pregnancy in their lifetime.

Is biochemical pregnancy more common in IVF pregnancies?
No. All IVF pregnancies are closely monitored by early testing and early sonography hence more cases of biochemical pregnancies are detected in IVF pregnancies as compared to natural pregnancy. Most of biochemical pregnancies are missed in non-IVF cases because they are not monitored so closely and so early.
What are the signs and symptoms of a biochemical pregnancy?
- Having a late period by about a week than your expected date of menses.
- Getting a positive pregnancy test on home pregnancy test, but having a period after few days.
- Getting a negative pregnancy test few weeks after a positive pregnancy test using home pregnancy test.
- Experiencing a heavier than usual bleeding with or without intense menstrual cramps.
- Not experiencing the early pregnancy symptoms after a positive pregnancy test.
What to do after Biochemical Pregnancy?
Once biochemical pregnancy is diagnosed by an fertility specialist , you should wait till beta hCG levels come back to normal. (Undetectable on blood test or urine test). After that, your IVF specialist might perform some other blood tests or an ultrasound and guide you further.
If I had a previous biochemical pregnancy, what are the chances of success in my next IVF Cycle?
Biochemical pregnancy does not have any negative impact on future pregnancies. Some studies have shown that women who have had biochemical pregnancies in the past have a better chance of having a successful pregnancy outcome in the future.
Even in IVF cases, biochemical pregnancy should be considered as a positive predictive factor for success in subsequent IVF cycles. So, in short, chances of having a successful pregnancy after a biochemical pregnancy are good.
What are the causes of biochemical pregnancy?
An embryo is formed when an egg is fertilized by a sperm. An embryo at Day 5 is called a Blastocyst. The outer layer of the blastocyst is called trophectoderm and it starts producing a hormone called Beta Human chorionic Gonadotrophin (Beta HCG). As the embryo grows, it produces more Beta HCG.
Most early pregnancy can be detected when the bHCG hormone is found in urine of a woman.
But when due to certain reasons an embryo ceases to grow very early or fails to implant in the uterus, it also stops producing Beta HCG and hence the blood and urine HCG levels decline. This is the reason that pregnancy tests comes out negative after an initial positive result. All this happens even before the pregnancy can be detected by ultrasonography, which is mostly before 5 weeks.
What are risk factors and untreated conditions that may increase chances of having a biochemical pregnancy?
Having any of the following may lead to increased risk of a biochemical pregnancy:
- Maternal age over 35
- Diabetes
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Thyroid disorder
- A blood clotting disorder
How is a biochemical pregnancy diagnosed?
It is mostly diagnosed after taking a detailed history about your menstrual cycles, last period date or LMP and/or urine or serum beta HCG levels.
Is there any treatment for biochemical pregnancy ? Can biochemical pregnancies be prevented in future pregnancies?
There is no definite treatment proposed.
During subsequent natural conception or IVF attempts, some strategies may be:
- To rectify endocrinologic disorders if any
- Attempt Blastocycst Transfer (Extended Embryo Culture)
- PGT-A ( genetic testing of embryos only to be considered if there is history of repeated biochemical pregnancies)
- Usage of Anti-thrombotic therapy like Aspirin and LMW Heparin.
What are the emotional effects of a biochemical pregnancy?
A biochemical pregnancy can evoke various emotional responses in both the individual and their partner. It may intensify the stress if they have been struggling with infertility. It can also lead to feelings of anxiety and sometimes sorrow, knowing that a pregnancy was possible. It’s crucial to openly communicate these emotions and address them with great care and sensitivity. Recognizing the loss is essential, but it’s equally important to understand that biochemical pregnancies often involve embryos with genetic defects, which can lead to early miscarriage. There’s a good chance that a subsequent pregnancy will be healthy.
How can I cope with a biochemical pregnancy?
- Sharing your concerns with your doctor will help you understand what you are going through better.
- It’s completely normal to feel grief; just make sure you have a strong support system in the form of friends, family, or any other assistance to aid in your healing process.
- If biochemical pregnancy occurs after a fertility treatment, it can be very stressful, and one can seek help and support from a counselor to cope with the situation better.
However patients suffering from biochemical pregnancy should know that just because it has happened once does not mean it will happen again.
Where can I find support groups for biochemical pregnancy ?
- Stillbirth society of India
- Share Pregnancy and Infant Loss Support
- March of Dimes
- International Stillbirth Alliance (ISA)
- The Miscarriage Association
- Sands
- The Compassionate Friends
- MISS Foundation
- Centre for Loss in Multiple Birth (CLIMB)
- Helping After Neonatal Death (HAND)
- The Ectopic Pregnancy Trust
- Tommy’s
Things to Remember
- It is a very early pregnancy loss, mostly before 5th week, even before it can be detected on ultrasonography.
- May be missed by patient as it can present as a heavy period with cramps with a delay of 1 week or more.
- It can be a reason for a negative pregnancy test after an earlier positive test.
- Can only be detected by Beta HCG test.
- Could be because of genetic error in the embryo.
- Chances are the next pregnancy would be healthy.