What is Ectopic Pregnancy?
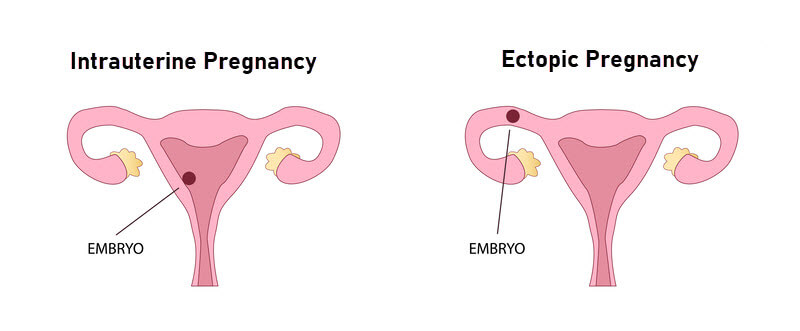
Normally the embryo implants and grows inside the uterus – intrauterine.
When the embryo implants and grows outside the uterus (commonest site is fallopian tube), it is known as ectopic pregnancy.
What are the symptoms of Tubal Pregnancy or Ectopic Pregnancy?
Ectopic pregnancy in first few days is similar to normal intrauterine pregnancy. Patients will experience missing their menstrual period, loss of appetite, morning sickness and other similar symptoms of pregnancy.
As pregnancy advances, around 6 weeks, in ectopic pregnancy, patients usually experience abdominal pain and spotting. The pain is because of stretching of fallopian tube.
If the tube ruptures, pain is severe and unbearable. Because of rupture of the fallopian tube, bleeding also occurs inside the abdomen which can lead to symptoms of shock such as fainting, dizziness, feeling cold and clammy, black outs etc. This is an urgent condition wherein patients need to be taken to the hospital immediately and need immediate blood transfusion and surgery.
How is Ectopic Pregnancy diagnosed?
Ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed by:
- Symptoms of pregnancy
- Symptoms of advanced ectopic like pain, spotting, severe pain and features of shock
- Serial Beta HCG determination – Beta hCG normally doubles every 48 hours. In ectopic pregnancy doubling of beta hCG does not occur.
- Ultarsound – Vaginal ultrasound can detect ectopic pregnancy but this is relatively difficult early on in pregnancy and can be missed at times.
Is Ectopic Pregnancy same as Tubal Pregnancy?
Ectopic pregnancy can occur anywhere outside the uterus.
Most common site of ectopic pregnancy is Tubal ectopic.
Other uncommon sites of ectopic pregnancy are: ovarian ectopic (embryo grows on the ovary), abdominal ectopic (embryo grows outside uterus and tubes, in the abdominal cavity)
Who is at a risk of tubal Ectopic Pregnancy and what are the causes of Ectopic Pregnancy ?
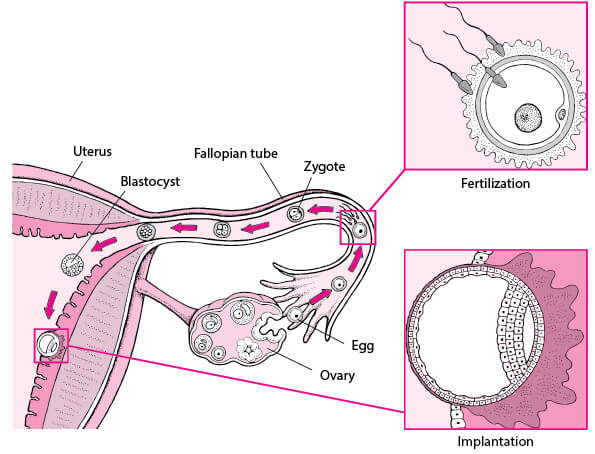
Normally the egg is released from the ovary and then gets pulled into the fallopian tube.
In the tube, the egg is fertilized by the sperm. When the egg is fertilized by the sperm, it is called an embryo.
The embryo travels from the fallopian tube to the uterus. This takes about 5 days.
Once the embryo reached the uterus, it gets implanted in the endometrium (lining of uterus) and this is how normal pregnancy occurs.
If fallopian tube is damaged, the embryo instead of travelling from the fallopian tube into the uterus, gets stuck in the fallopian tube and starts growing in the tube. This is called Tubal ectopic pregnancy.
Damage to the fallopian tube can be caused by:
Infection of the fallopian tubes – Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID), recurrent episodes of acute infection, History of tuberculosis affecting tubes (Genital tuberculosis), Past history of appendicitis affecting tubes and any infection affecting pelvis or surrounding organs.
Surgery on or around the fallopian tubes like adhesion removal, removal of ovarian cyst, tubal recanalization etc
Endomteriosis is very commonly associated with infertility and also increased risk of ectopic pregnancy.
What is the treatment for Ectopic Pregnancy?
Ectopic if diagnosed early, can be medically managed with the help of oral medication and injections. If ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed early, surgery can be avoided.
Once the duration of pregnancy advances, usually surgery is the only option left. If the tube has not ruptured or there is very little bleeding and patient is stable, Laparoscopy can be performed which is minimally invasive and has very short recovery time.
However if there is a lot of bleeding and the patient is not stable, Open surgery or Laparotomy is the only option left. Usually this is accompanied with a lot of blood loss and therefore blood transfusion is also necessary.
Does IVF Embryo Transfer increase the chances of Ectopic Pregnancy? Can IVF cause Ectopic pregnancy? OR Is the chance of ectopic pregnancy increased in IVF?
If single day 5 blastocyst is transferred, the risk of having an ectopic is 14 per 1000 pregnancies. This is even less than the risk of having an ectopic pregnancy if someone conceives naturally which is 20/1000 pregnancies. Hence if Single blastocyst transfer is performed, IVF actually reduces the chances of having an ectopic pregnancy. We at Indore infertility clinic perform single Blastocyst Transfer for most of the patients.
How can we prevent Ectopic Pregnancy?
While attempting normal pregnancy, you cannot prevent an ectopic pregnancy but you can definitely reduce your risk by maintaining healthy lifestyle, not acquiring sexually transmitted diseases, using barrier contraceptives when not wanting pregnancy, avoidance of drugs and smoking. All these definitely reduce the risk of tubal damage and therefore reduce the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
While performing ART and IVF, by transferring day 5 embryos in a natural cycle (Freeze all IVF) reduces the risk of having an ectopic pregnancy
If I have had an Ectopic Pregnancy before, can I have Ectopic Pregnancy again ?
The risk of having recurrent ectopic pregnancy is very high. If someone has had an ectopic in the past, chance of having a repeat ectopic in subsequent pregnancy is as high as 15%.
If I have had an Ectopic Pregnancy, do I have to undergo IVF Treatment to become pregnant in the future?
If one tube is normal, then there are chances of becoming pregnant normally. If both tubes are damaged, there are very high chances that you will need IVF to become pregnant.
ECTOPIC PREGNANCY IN PAST ?
If you have had an ectopic pregnancy in the past and are worried about you chances of becoming pregnant again, you may talk to our Specialist to know More.
FREE CONSULT WITH SPECIALIST